Decoding the Earth’s Tremors: A Complete Information to Tremor Maps
Associated Articles: Decoding the Earth’s Tremors: A Complete Information to Tremor Maps
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by means of the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the Earth’s Tremors: A Complete Information to Tremor Maps. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Earth’s Tremors: A Complete Information to Tremor Maps
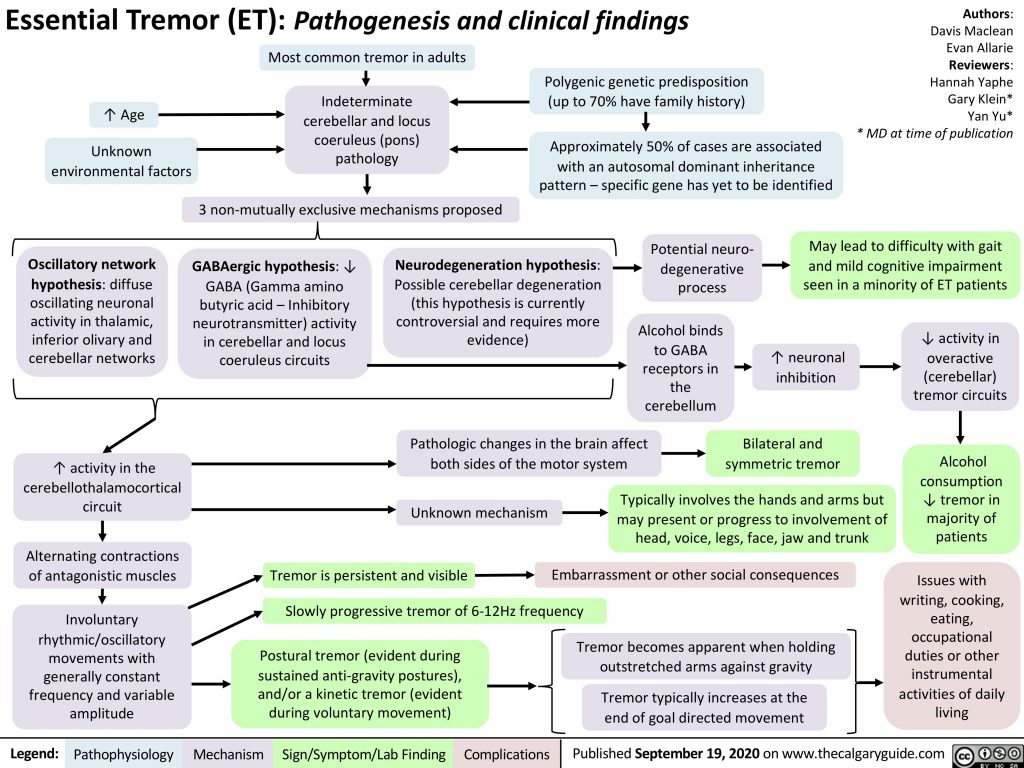
The Earth is a dynamic planet, continuously shifting and reshaping itself. This dynamism is most dramatically displayed by means of seismic exercise, from the delicate tremors barely felt by people to the devastating energy of main earthquakes. Understanding this exercise is essential for mitigating dangers, planning infrastructure, and advancing our data of geophysics. A key software on this understanding is the tremor map, a visible illustration of seismic exercise throughout a geographical space. This text delves into the intricacies of tremor maps, exploring their creation, interpretation, and invaluable contributions to numerous fields.
What’s a Tremor Map?
A tremor map, at its core, is a geographical illustration of seismic occasions over a selected interval. It would not merely present the areas of earthquakes; it conveys a wealth of details about their magnitude, frequency, and depth, typically utilizing color-coding, dimension of markers, and different visible cues to characterize these parameters. These maps can vary from global-scale depictions of tectonic plate boundaries and main earthquake zones to extremely localized maps specializing in a selected area, metropolis, or perhaps a single fault line.
The info used to create these maps originates from seismographs, subtle devices that detect and document floor movement. Hundreds of seismograph stations worldwide repeatedly monitor seismic waves, transmitting knowledge to international and regional seismic networks. This knowledge is then processed utilizing subtle algorithms to find the epicenter (the purpose on the Earth’s floor straight above the earthquake’s origin), decide the magnitude (a measure of the earthquake’s power launch), and estimate the depth of the hypocenter (the precise level of rupture underground).
Sorts of Tremor Maps:
Tremor maps will not be monolithic; they arrive in varied types relying on their goal and the information they characterize:
-
World Seismic Hazard Maps: These maps present a broad overview of worldwide seismic exercise, usually highlighting areas with excessive seismic threat based mostly on historic knowledge and tectonic plate boundaries. They typically use shade gradients to characterize various ranges of threat, serving to policymakers and concrete planners assess vulnerability.
-
Regional Seismic Hazard Maps: These maps give attention to particular areas, offering extra detailed details about seismic hazards inside a smaller geographical space. They’re essential for native constructing codes, emergency response planning, and infrastructure growth.
-
Actual-time Seismic Maps: These dynamic maps replace in real-time, displaying seismic occasions as they happen. They’re invaluable for fast response to earthquakes, permitting emergency providers to rapidly assess the affected areas and deploy assets successfully. These maps typically incorporate info on shaking depth, which could be essential for understanding the potential injury attributable to an earthquake.
-
Historic Seismic Maps: These maps illustrate seismic exercise over prolonged durations, offering precious insights into long-term tendencies and patterns of earthquake prevalence. They’re important for understanding the recurrence intervals of earthquakes in a specific area, contributing to long-term threat evaluation.
-
Induced Seismicity Maps: These specialised maps give attention to earthquakes triggered by human actions, corresponding to oil and gasoline extraction, geothermal power manufacturing, and large-scale water impoundment. Understanding induced seismicity is significant for mitigating dangers related to these actions.
Deciphering Tremor Maps:
Successfully deciphering a tremor map requires understanding the conventions used. Frequent components embrace:
-
Epicenter Areas: These are often marked by factors or symbols, typically with their dimension reflecting the magnitude of the earthquake.
-
Magnitude Scales: Tremor maps generally use the Second Magnitude Scale (Mw), a logarithmic scale that represents the full power launched by an earthquake. Every complete quantity enhance represents a tenfold enhance in amplitude and about 32 instances extra power.
-
Depth: The depth of the earthquake’s hypocenter is usually indicated, both by means of color-coding or separate depth maps. Shallow earthquakes typically trigger extra injury on the floor than deeper ones.
-
Time Interval: The map’s timeframe is essential. A map exhibiting exercise over a number of days will differ considerably from one overlaying a number of many years.
-
Colour Schemes: Colour-coding is continuously used to characterize magnitude, depth, or shaking depth. A legend is all the time important for understanding the which means of the colours.
-
Fault Traces: Many tremor maps overlay recognized fault traces, offering context for the situation of seismic occasions.
Functions of Tremor Maps:
Tremor maps have far-reaching purposes throughout varied disciplines:
-
Earthquake Early Warning Methods: Actual-time tremor maps are integral to earthquake early warning methods, offering essential info for issuing well timed alerts to populations in danger.
-
Seismic Hazard Evaluation: These maps are elementary to assessing seismic hazards, informing constructing codes, land-use planning, and insurance coverage insurance policies.
-
Infrastructure Design: Engineers make the most of tremor maps to design earthquake-resistant constructions, making certain buildings and infrastructure can stand up to seismic occasions.
-
Catastrophe Response and Aid: Following an earthquake, tremor maps assist emergency responders prioritize areas requiring fast consideration and allocate assets successfully.
-
Scientific Analysis: Tremor maps are important instruments for seismologists and geophysicists, enabling them to review earthquake patterns, tectonic plate actions, and the Earth’s inner construction.
-
Public Consciousness and Schooling: Tremor maps can be utilized to teach the general public about seismic hazards and promote preparedness.
Limitations of Tremor Maps:
Whereas immensely precious, tremor maps have limitations:
-
Information Availability: The accuracy of a tremor map will depend on the density and high quality of seismograph knowledge. In sparsely instrumented areas, the map’s decision could also be restricted.
-
Magnitude Underestimation: Smaller earthquakes, significantly these in distant areas, could go undetected or underreported, resulting in an incomplete image of seismic exercise.
-
Uncertainty in Location and Magnitude: There may be all the time a point of uncertainty related to finding the epicenter and figuring out the magnitude of an earthquake.
-
Complexity of Seismic Processes: Tremor maps simplify complicated geological processes. They can’t absolutely seize the intricacies of fault rupture, stress accumulation, and the interactions between totally different tectonic plates.
The Way forward for Tremor Maps:
The way forward for tremor maps is vibrant, pushed by developments in seismology, computing energy, and knowledge visualization. We will count on to see:
-
Improved Information Decision: The rising density of seismograph networks, coupled with superior knowledge processing strategies, will result in higher-resolution maps, offering extra correct and detailed details about seismic exercise.
-
Integration of Different Information Sources: Tremor maps are prone to combine knowledge from different sources, corresponding to GPS measurements, satellite tv for pc imagery, and geological surveys, to reinforce their accuracy and supply a extra complete understanding of seismic hazards.
-
Enhanced Visualization Methods: New visualization strategies will allow extra intuitive and informative representations of seismic knowledge, making tremor maps extra accessible and simpler to grasp for a wider viewers.
-
Superior Predictive Modeling: Combining tremor map knowledge with superior modeling strategies will assist enhance earthquake forecasting and threat evaluation, resulting in more practical mitigation methods.
In conclusion, tremor maps are indispensable instruments for understanding and managing the dangers related to earthquakes. Their purposes lengthen far past merely exhibiting the place earthquakes happen; they supply important info for catastrophe preparedness, infrastructure design, scientific analysis, and public consciousness. As expertise advances and our understanding of seismic processes deepens, tremor maps will proceed to play an important function in defending lives and property from the devastating results of earthquakes.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered precious insights into Decoding the Earth’s Tremors: A Complete Information to Tremor Maps. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!
